Mutational survivorship bias: The case of PNKP
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
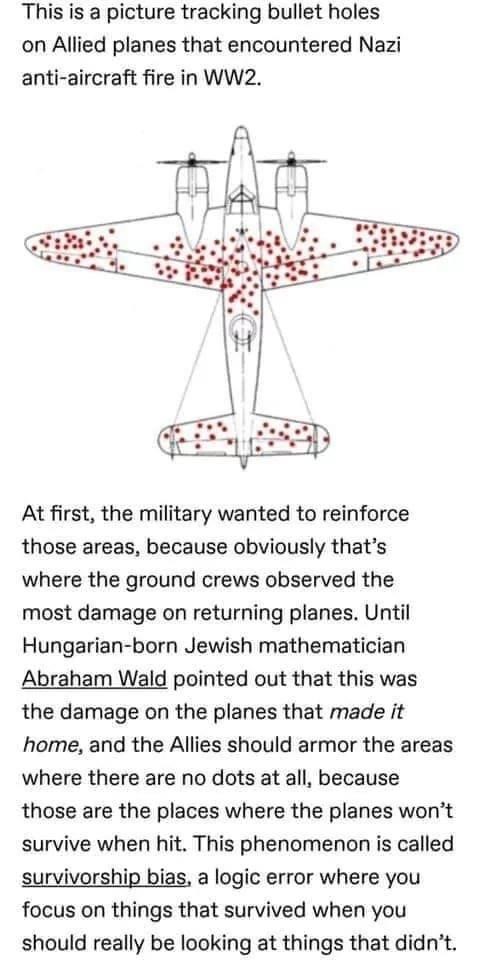
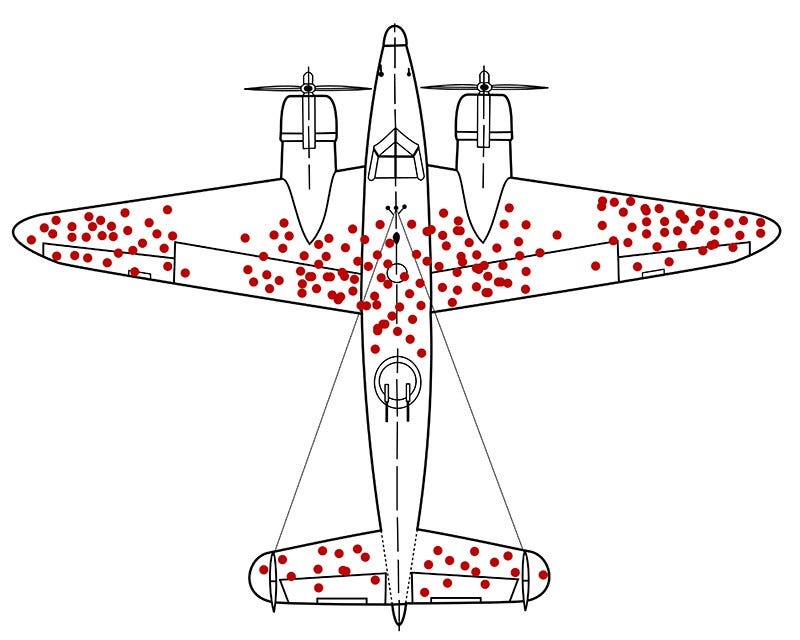
The molecular function of a protein relies on its structure. Understanding how variants alter structure and function in multidomain proteins is key to elucidate the generation of a pathological phenotype. However, one may fall into the logical bias of assessing protein damage only based on the variants that are visible (survivorship bias), which can lead to partial conclusions. This is the case of PNKP, an important nuclear and mitochondrial DNA repair enzyme with both kinase and phosphatase function. Most variants in PNKP are confined to the kinase domain, leading to a pathological spectrum of three apparently distinct clinical entities. Since proteins and domains may have a different tolerability to variation, we evaluated whether variants in PNKP are under survivorship bias. Here, we provide the evidence that supports a higher tolerance in the kinase domain even when all variants reported are deleterious. Instead, the phosphatase domain is less tolerant due to its lower variant rates, a higher degree of sequence conservation, lower dN/dS ratios, and the presence of more disease-propensity hotspots. Together, our results support previous experimental evidence that demonstrated that the phosphatase domain is functionally more necessary and relevant for DNA repair, especially in the context of the development of the central nervous system. Finally, we propose the term "Wald’s domain" for future studies analyzing the possible survivorship bias in multidomain proteins.
Mutational survivorship bias: The case of PNKP

DNA repair Leaders in Pharmaceutical Business Intelligence (LPBI) Group

Molecular basis of the association between transcription regulators nuclear respiratory factor 1 and inhibitor of DNA binding protein 3 and the development of microvascular lesions - ScienceDirect

Integrative representation showing the mitochondrial dysfunction as an

PDF] Primary blast wave protection in combat helmet design: A historical comparison between present day and World War I
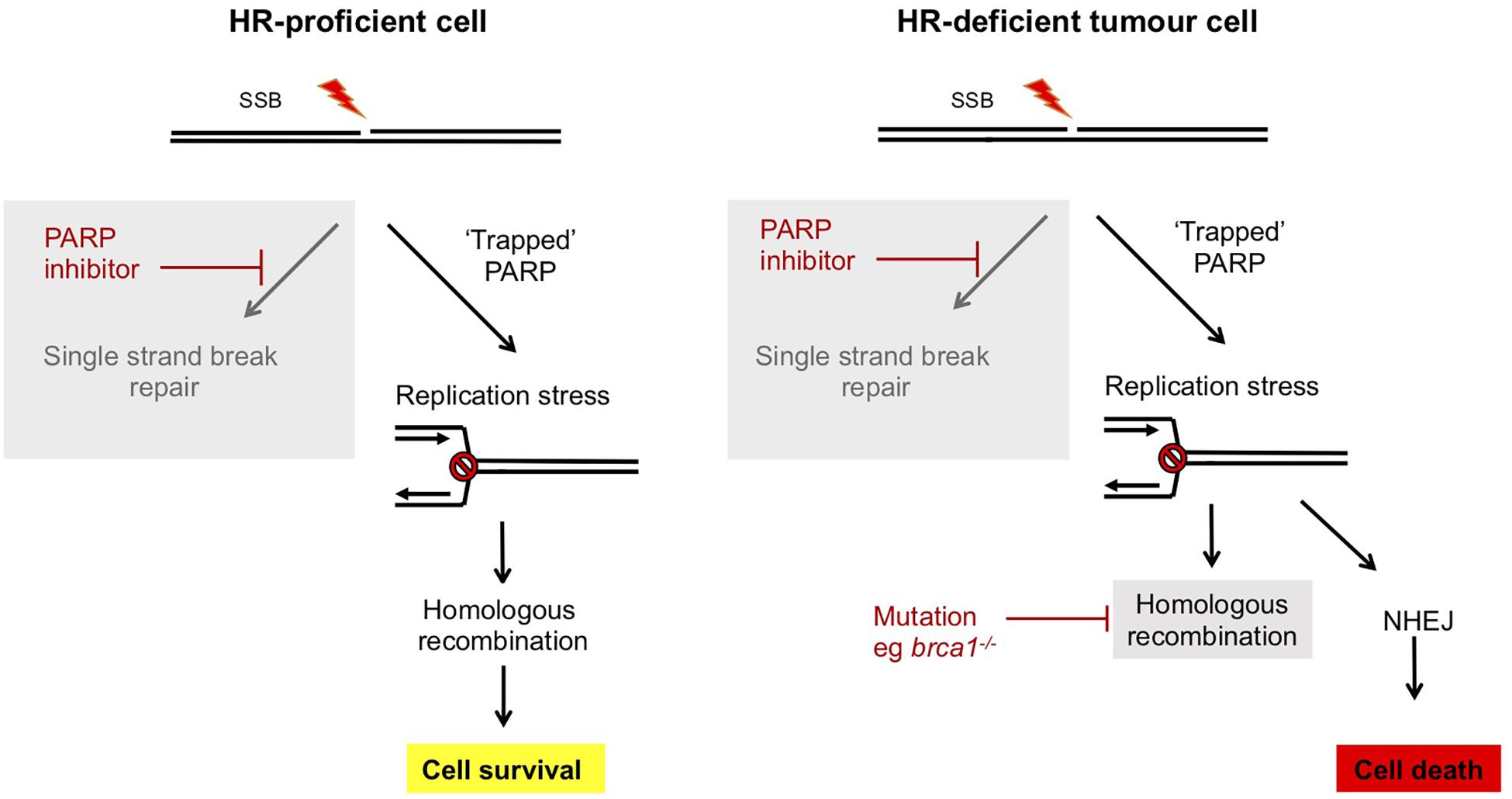
Importance of the PNKP DNA 5 -kinase, 3 -phosphatase, and FHA Domains
Frontiers Dictyostelium discoideum as a Model to Assess Genome Stability Through DNA Repair

Browse Preprints - Authorea

DNA methylation changes in genes frequently mutated in sporadic colorectal cancer and in the DNA repair and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway genes

Fluorescent Probes of DNA Repair

Phosphorylation of PNKP mediated by CDKs promotes end-processing of Okazaki fragments during DNA replication

Pan-cancer analysis of post-translational modifications reveals shared patterns of protein regulation - ScienceDirect

PDF) Mutational survivorship bias: The case of PNKP
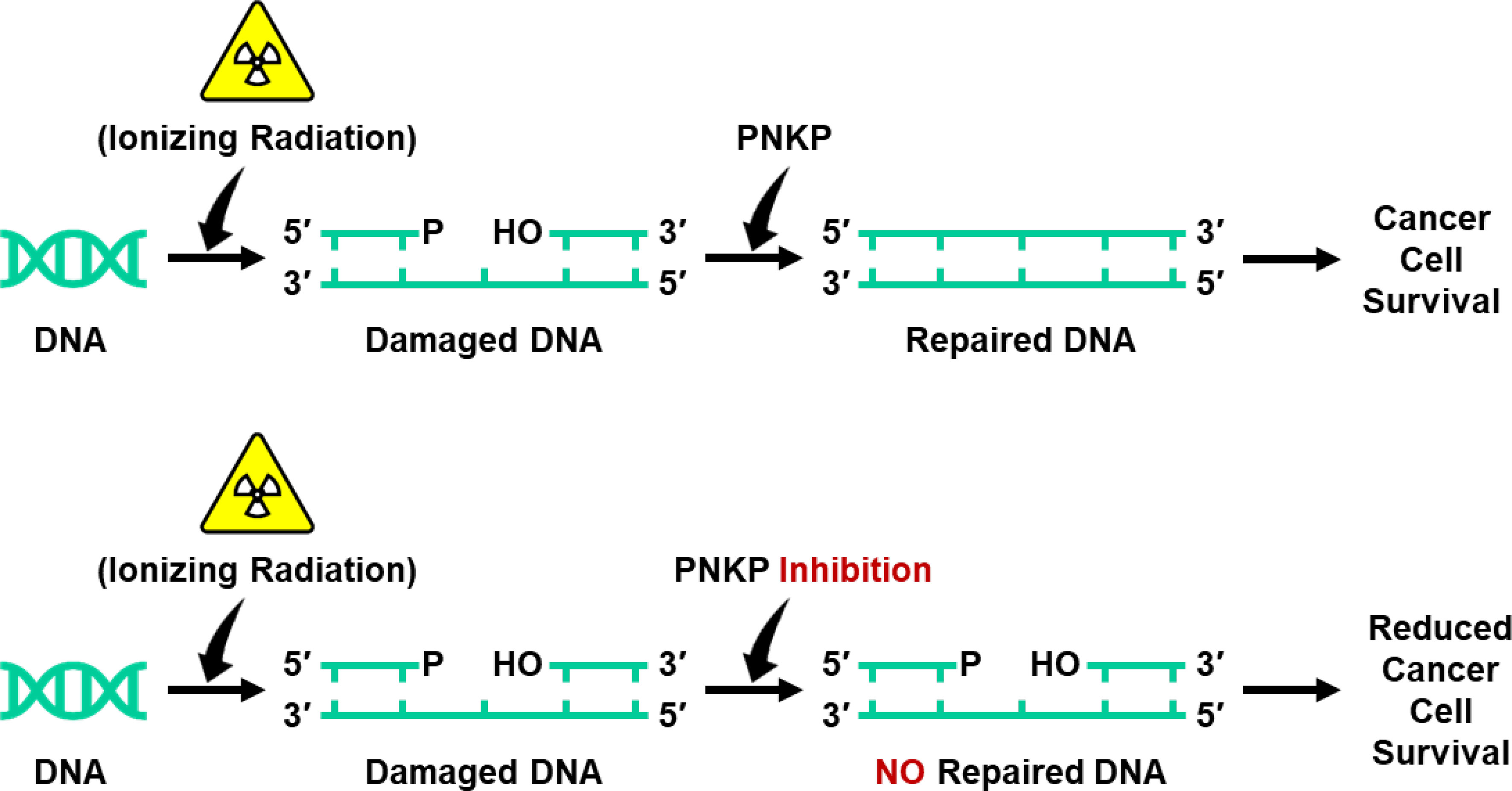
Frontiers Nano-Delivery of a Novel Inhibitor of Polynucleotide Kinase/Phosphatase (PNKP) for Targeted Sensitization of Colorectal Cancer to Radiation-Induced DNA Damage
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)