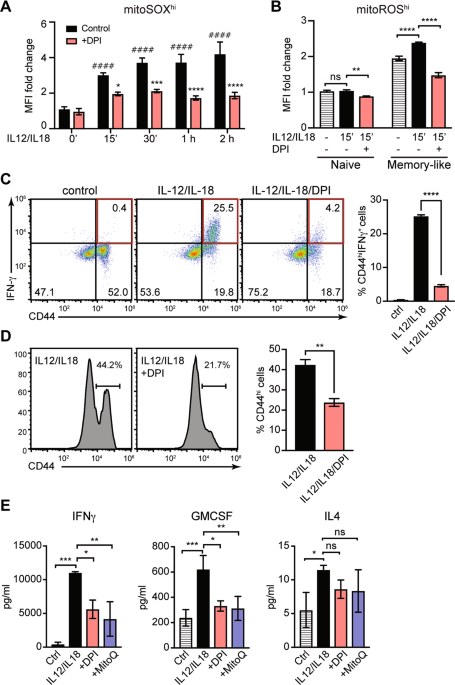
The role played by alternative splicing in antigenic variability in
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Endo-parasites that affect humans include Plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria, which remains one of the leading causes of death in human beings. Despite decades of research, vaccines to this and other endo-parasites remain elusive. This is in part due to the hyper-variability of the parasites surface proteins. Generally these surface proteins are encoded by a large family of genes, with only one being dominantly expressed at certain life stages. Another layer of complexity can be introduced through the alternative splicing of these surface proteins. The resulting isoforms may differ from each other with regard to cell localisation, substrate affinities and functions. They may even differ in structure to the extent that they are no longer recognised by the host’s immune system. In many cases this leads to changes in the N terminus of these proteins. The geographical localisation of endo-parasitic infections around the tropics and the highest incidences of HIV-1 infection in the same areas, adds a further layer of complexity as parasitic infections affect the host immune system resulting in higher HIV infection rates, faster disease progression, and an increase in the severity of infections and complications in HIV diagnosis. This review discusses some examples of parasite surface proteins that are alternatively spliced in trypanosomes, Plasmodium and the parasitic worm Schistosoma as well as what role alternate splicing may play in the interaction between HIV and these endo-parasites.

Single-cell and long-read sequencing to enhance modelling of
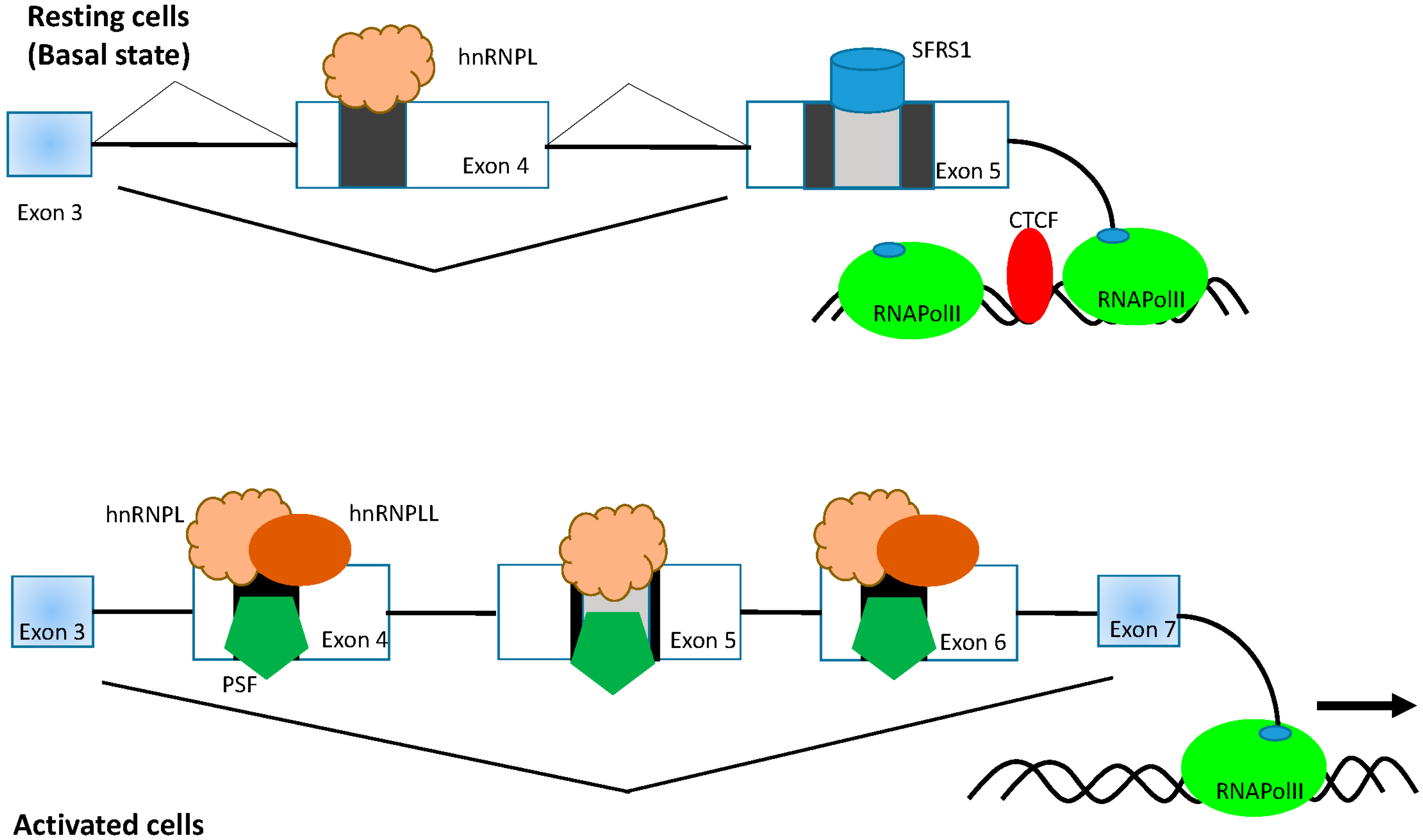
IJMS, Free Full-Text
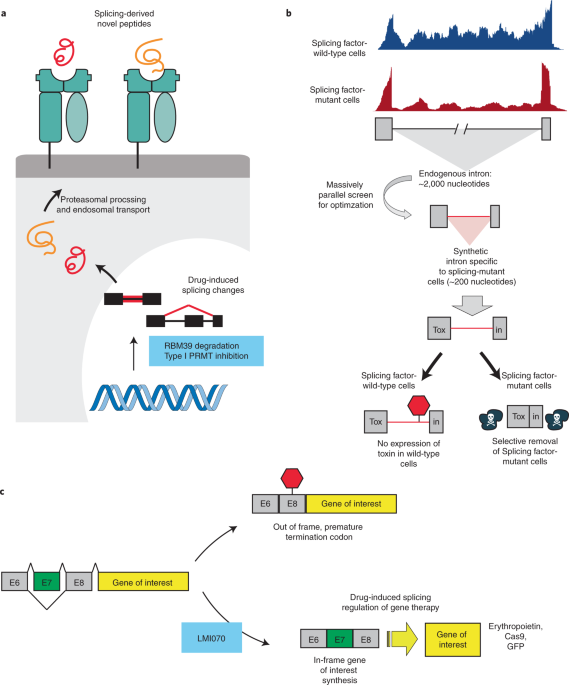
Dysregulation and therapeutic targeting of RNA splicing in cancer
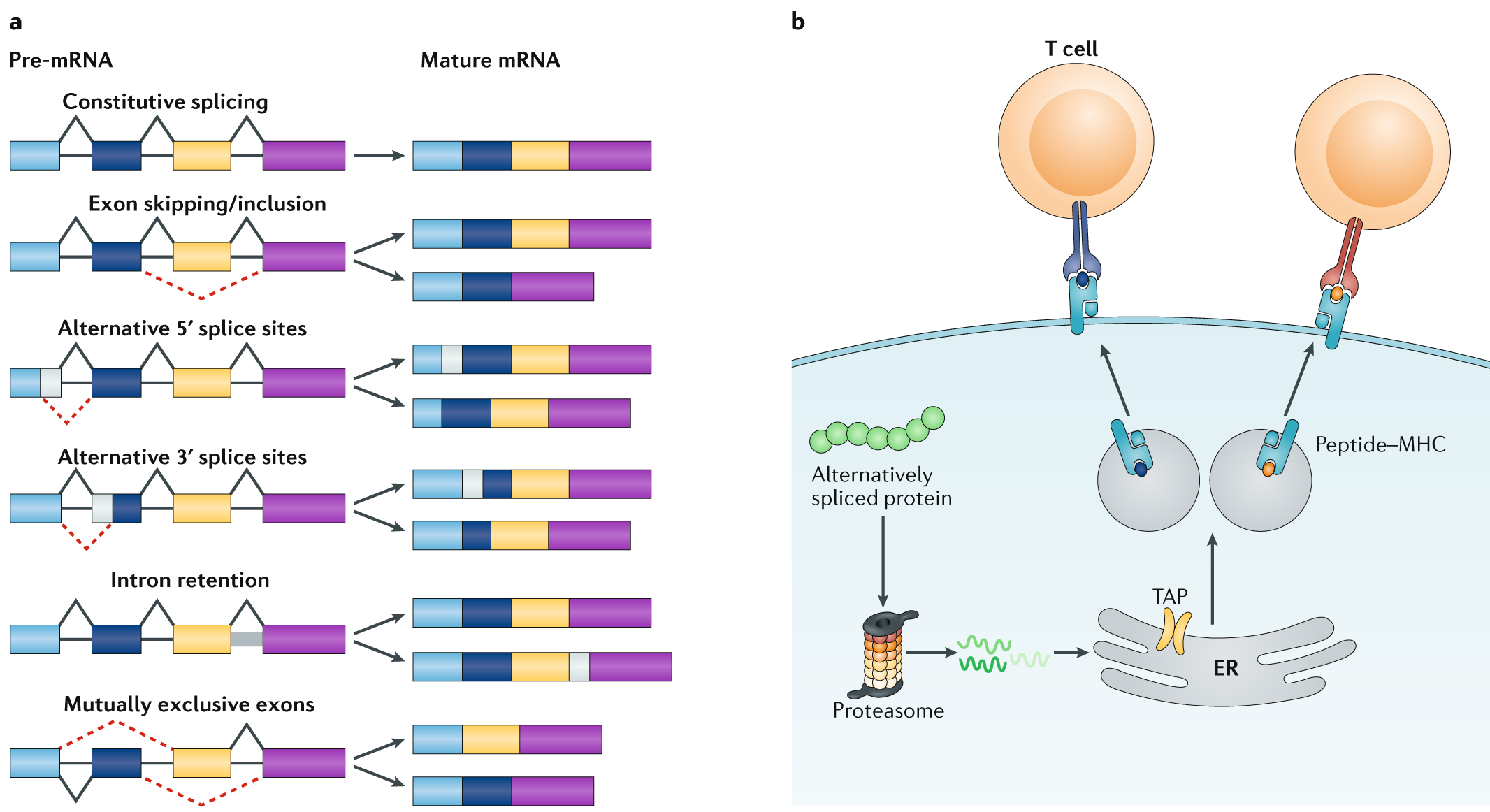
Alternative mRNA splicing in cancer immunotherapy

The Expanding Landscape of Alternative Splicing Variation in Human

Targeting the RNA G-Quadruplex and Protein Interactome for

Aire‐dependent transcripts escape Raver2‐induced splice‐event

RAD51-mediated R-loop formation acts to repair transcription

Mechanistic Similarities between Antigenic Variation and Antibody

Antigenic variation in African trypanosomes - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)