Retrospective evaluation of labetalol as antihypertensive agent in
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Background To evaluate the effect on arterial blood pressure (ABP) of labetalol infusion as treatment for perioperative non nociceptive acute hypertension in dogs. The clinical records of dogs receiving intra or postoperative labetalol infusion were retrospectively reviewed. Invasive systolic (SAP), mean (MAP) and diastolic (DAP) arterial pressure and heart rate (HR) before labetalol infusion (T0) and 15, 30, 45 and 60 min (T1, T2, T3 and T4 respectively) after infusion were retrieved. The dose rate of labetalol infusion and use of concurrently administered drugs that could have potentially affected ABP and/or HR were also recorded. ANOVA for repeated measures and Dunnett’s multiple comparison test were used to determine the effect of labetalol on ABP and HR. Differences were considered significant when p < 0.05. Results A total of 20 dogs met the inclusion criteria, and hypertension was documented after craniotomy (12/20), adrenalectomy (4/20) and other procedures (4/20). Five dogs received labetalol intraoperatively, 14 postoperatively, and 1 during the surgical procedure and recovery. Median infusion duration and rate were 463 (60-2120) minutes and 1.1 (0.2–3.4) mg/kg/h respectively. Median loading dose was 0.2 (0.2–0.4) mg/kg. Labetalol produced a significant decrease in SAP and DAP at all time points compared to T0 (p < 0.05), while the effect was not significant at T1 for MAP (p = 0.0519). Median maximum MAP decrease was 31 (20–90) mmHg. Heart rate did not increase significantly during treatment (p = 0.2454). Acepromazine given before or during labetalol treatment did not reduce significantly ABP (p = 0.735). Conclusions Labetalol produced a reliable and titratable decrease in ABP with non significant increase in HR.
PDF) Retrospective evaluation of labetalol as antihypertensive agent in dogs

PDF) A systematic review of nicardipine vs labetalol for the management of hypertensive crises

171: Pulse pressure and acute response to labetalol in women with severe hypertension in pregnancy - American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology
Maternal and neonatal outcomes of antihypertensive treatment in pregnancy: A retrospective cohort study

Safety and efficacy of continuous intravenous labetalol for blood pressure control in neurosurgical patients - Raywat Noiphithak, Gahn Duangprasert, Sasikan Sukhor, Pichayaphong Durongkaweroj, Vich Yindeedej, 2023

Initial antihypertensive agent effects on acute blood pressure after intracerebral haemorrhage

Continuous-Infusion Labetalol vs Nicardipine for Hypertension Management in Stroke Patients - ScienceDirect
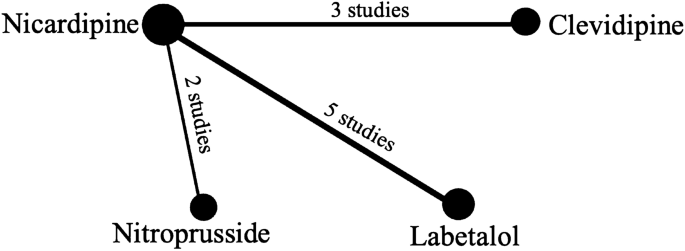
Comparison of Intravenous Antihypertensives on Blood Pressure Control in Acute Neurovascular Emergencies: A Systematic Review

Intravenous nicardipine and labetalol use in hypertensive patients with signs or symptoms suggestive of end-organ damage in the emergency department: a subgroup analysis of the CLUE trial
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)