Flanking-sequence exponential anchored–polymerase chain reaction amplification: a sensitive and highly specific method for detecting retroviral integrant–host–junction sequences - Cytotherapy
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
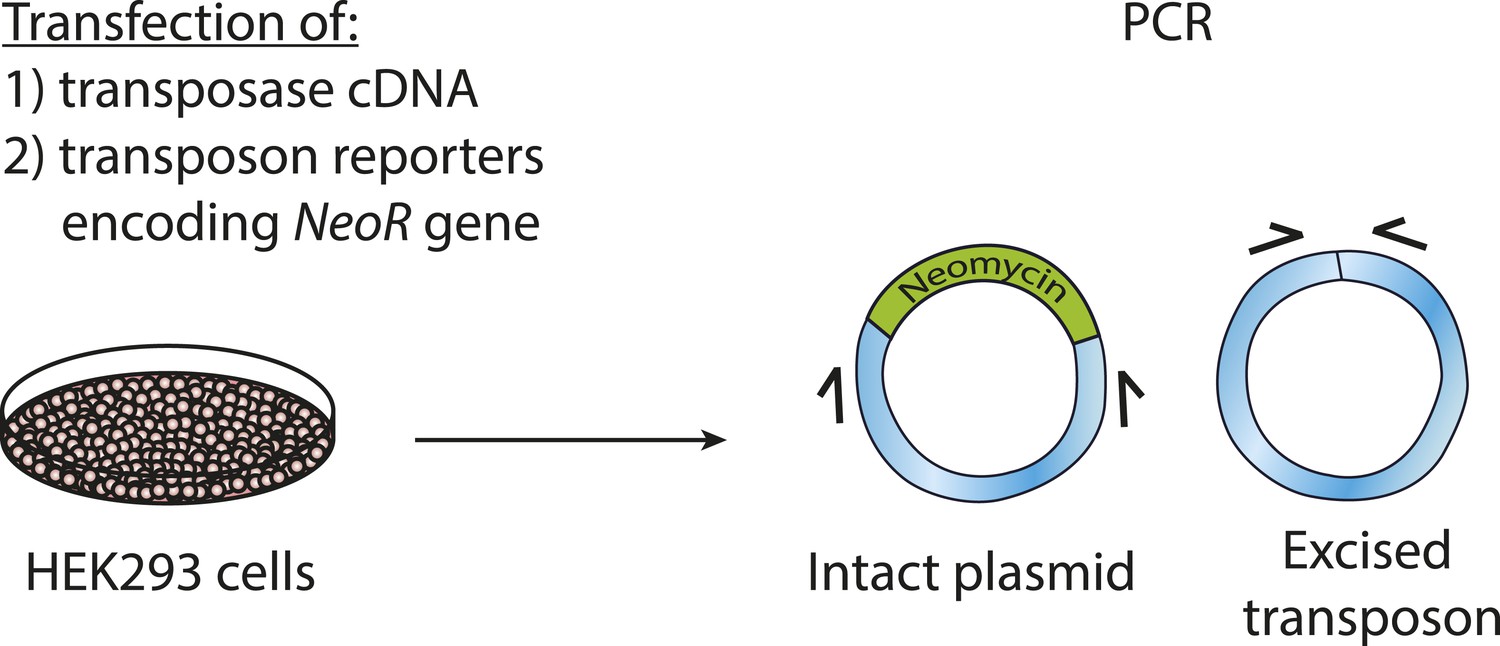
Genomic DNA transposition induced by human PGBD5

The Continuing Contribution of Gene Marking to Cell and Gene

Specific versus Nonspecific Isothermal DNA Amplification through

CviJI and CviJI* restriction activities of the native and cloned

Flanking-sequence exponential anchored–polymerase chain reaction

PDF) Impact of next-generation sequencing error on analysis of

Genomic DNA transposition induced by human PGBD5. - Abstract

Molecular cloning and gene organization of Chlorella virus IL-3A

PDF) Genome walking in eukaryotes

Linear and exponential TAIL-PCR: a method for efficient and quick

Long-term outcome of EBV-specific T-cell infusions to prevent or
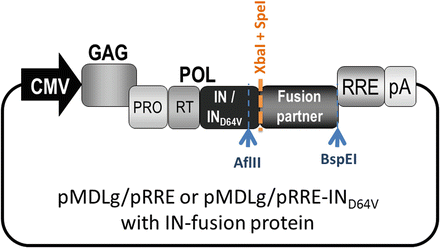
Development of Lentiviral Vectors for Targeted Integration and
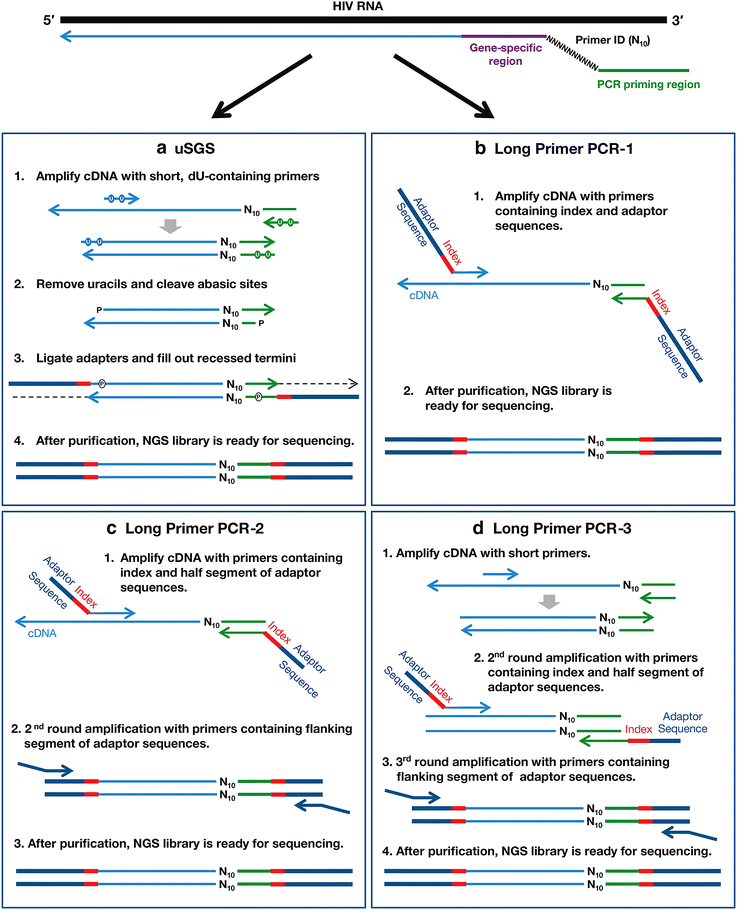
Ultrasensitive single-genome sequencing: accurate, targeted, next

Long-term outcome of EBV-specific T-cell infusions to prevent or

Simple innovative adaptor to improve genome walking with
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)