Transgenic Mice Expressing Green Fluorescent Protein under the Control of the Melanocortin-4 Receptor Promoter
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4-R) is an important regulator of energy homeostasis, and evidence suggests that MC4-R-expressing neurons are downstream targets of leptin action. MC4-Rs are broadly expressed in the CNS, and the distribution of MC4-R mRNA has been analyzed most extensively in the rat. However, relatively little is known concerning chemical profiles of MC4-R-expressing neurons. The extent to which central melanocortins act presynaptically or postsynaptically on MC4-Rs is also unknown. To address these issues, we have generated a transgenic mouse line expressing green fluorescent protein (GFP) under the control of the MC4-R promoter, using a modified bacterial artificial chromosome. We have confirmed that the CNS distribution of GFP-producing cells is identical to that of MC4-R mRNA in wild-type mice and that nearly all GFP-producing cells coexpress MC4-R mRNA. For example, cells coexpressing GFP and MC4-R mRNA were distributed in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus (PVH) and the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus (DMV). MC4-R promotor-driven GFP expression was found in PVH cells producing thyrotropin-releasing hormone and in cholinergic DMV cells. Finally, we have observed that a synthetic MC3/4-R agonist, MT-II, depolarizes some GFP-expressing cells, suggesting that MC4-Rs function postsynaptically in some instances and may function presynaptically in others. These studies extend our knowledge of the distribution and function of the MC4-R. The transgenic mouse line should be useful for future studies on the role of melanocortin signaling in regulating feeding behavior and autonomic homeostasis.

Journal of Comparative Neurology Systems Neuroscience Journal

MacroH2A1.2-GFP transgenic mice (adapted from [26], licence no

The Melanocortin-4 Receptor Is Expressed in Enteroendocrine L

Divergence of Melanocortin Pathways in the Control of Food Intake
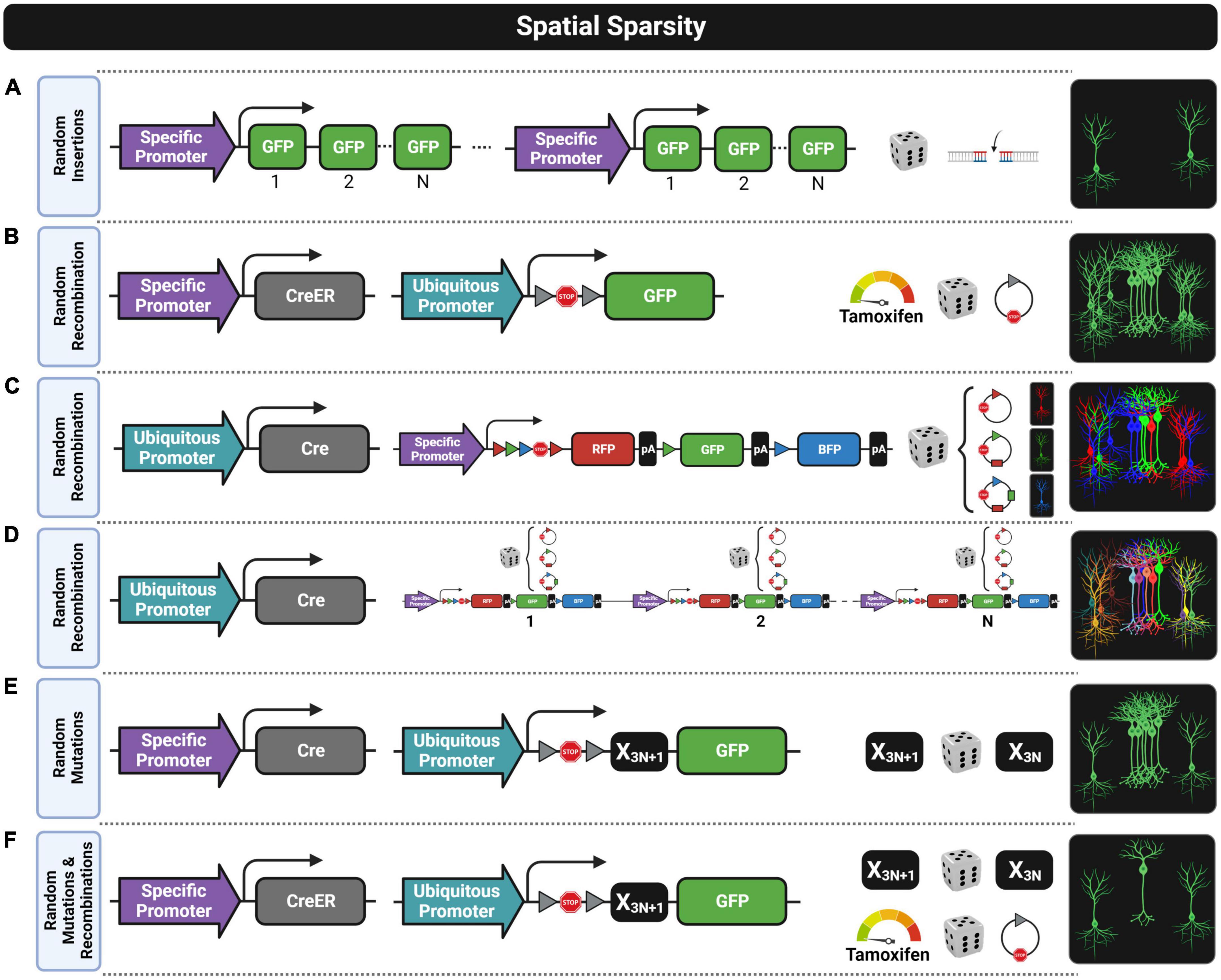
Frontiers Fluorescent transgenic mouse models for whole-brain
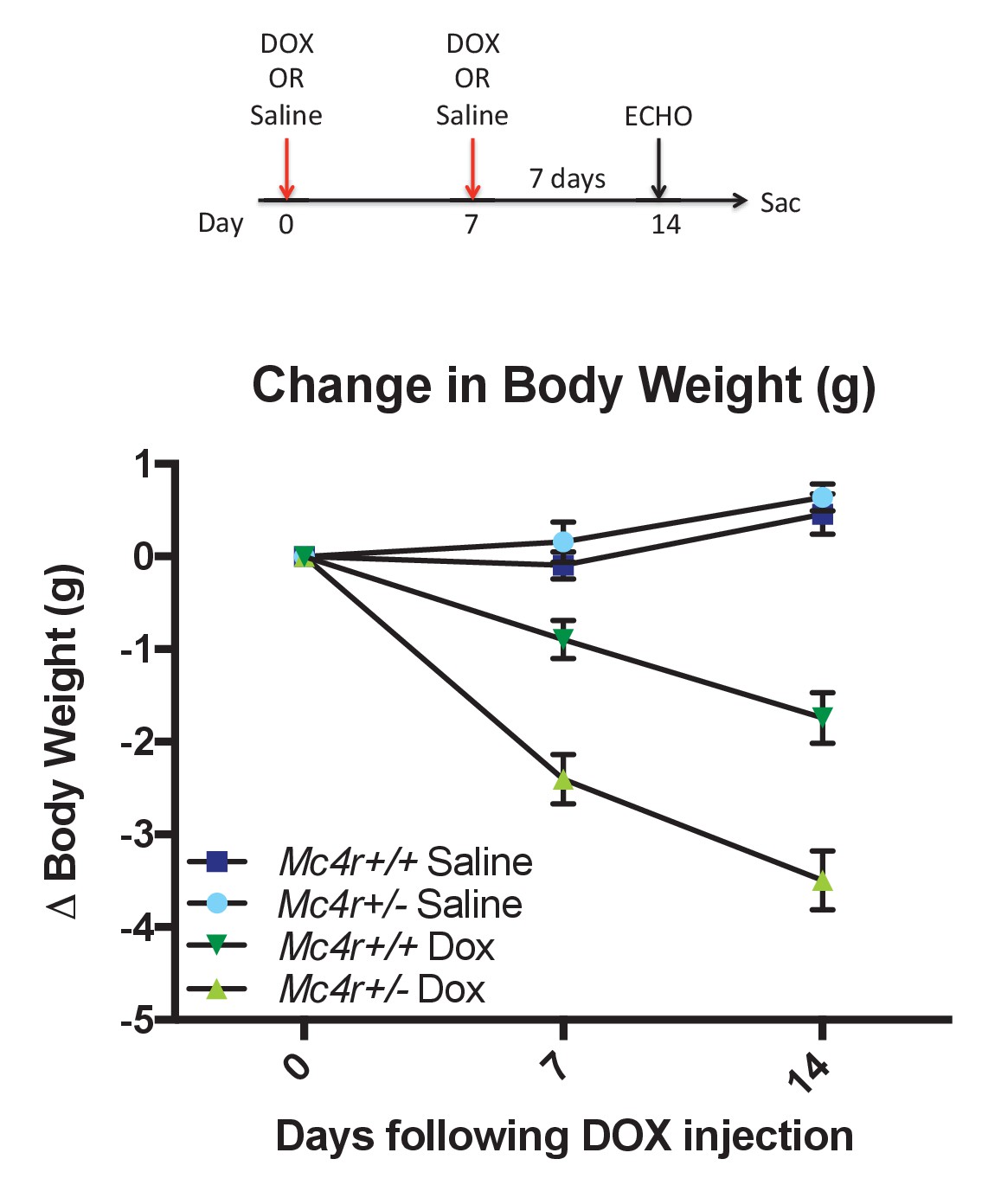
Loss of the melanocortin-4 receptor in mice causes dilated
Increased risk for T cell autoreactivity to ß-cell antigens in the
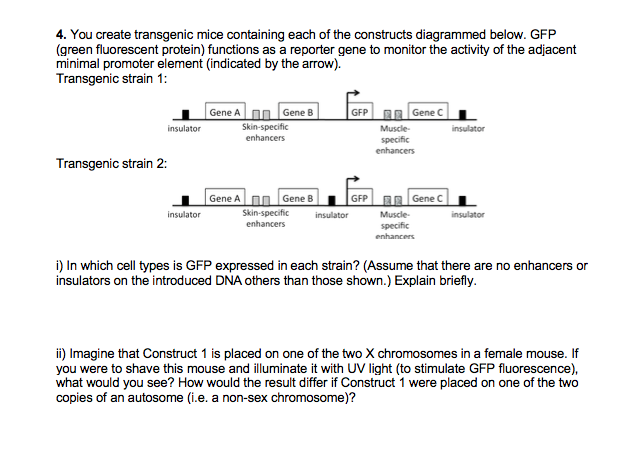
Solved 4. You create transgenic mice containing each of the
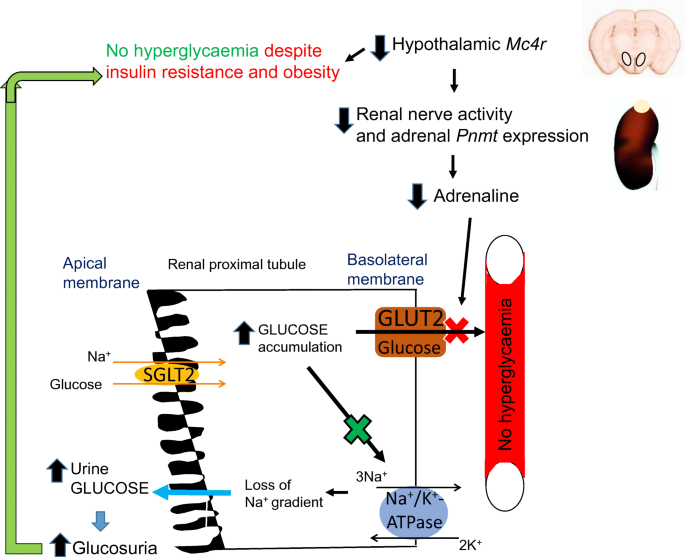
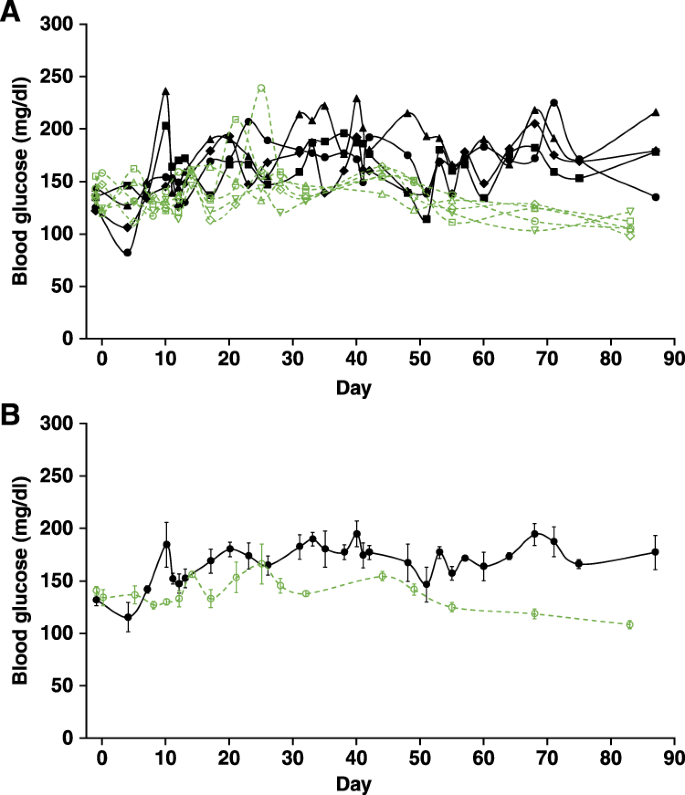
Hypothalamic MC4R regulates glucose homeostasis through adrenaline
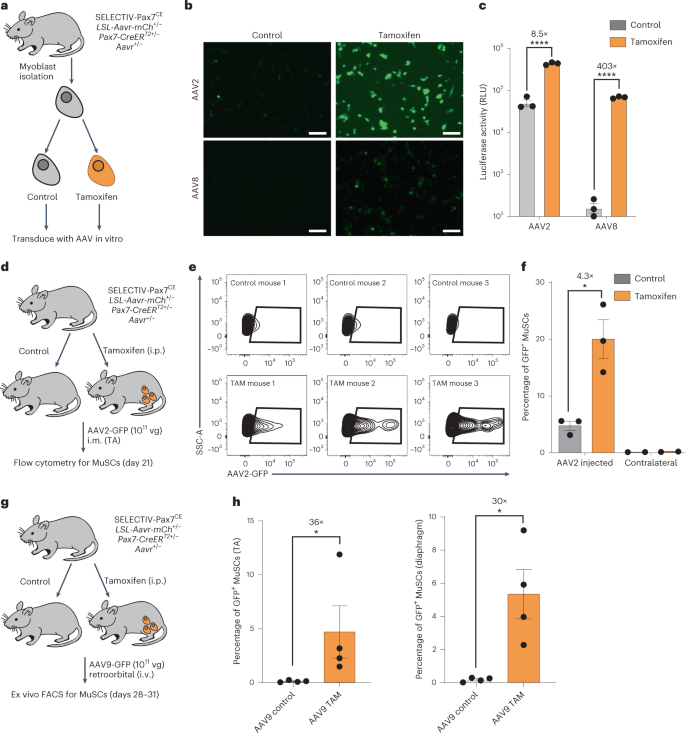
Hardwiring tissue-specific AAV transduction in mice through
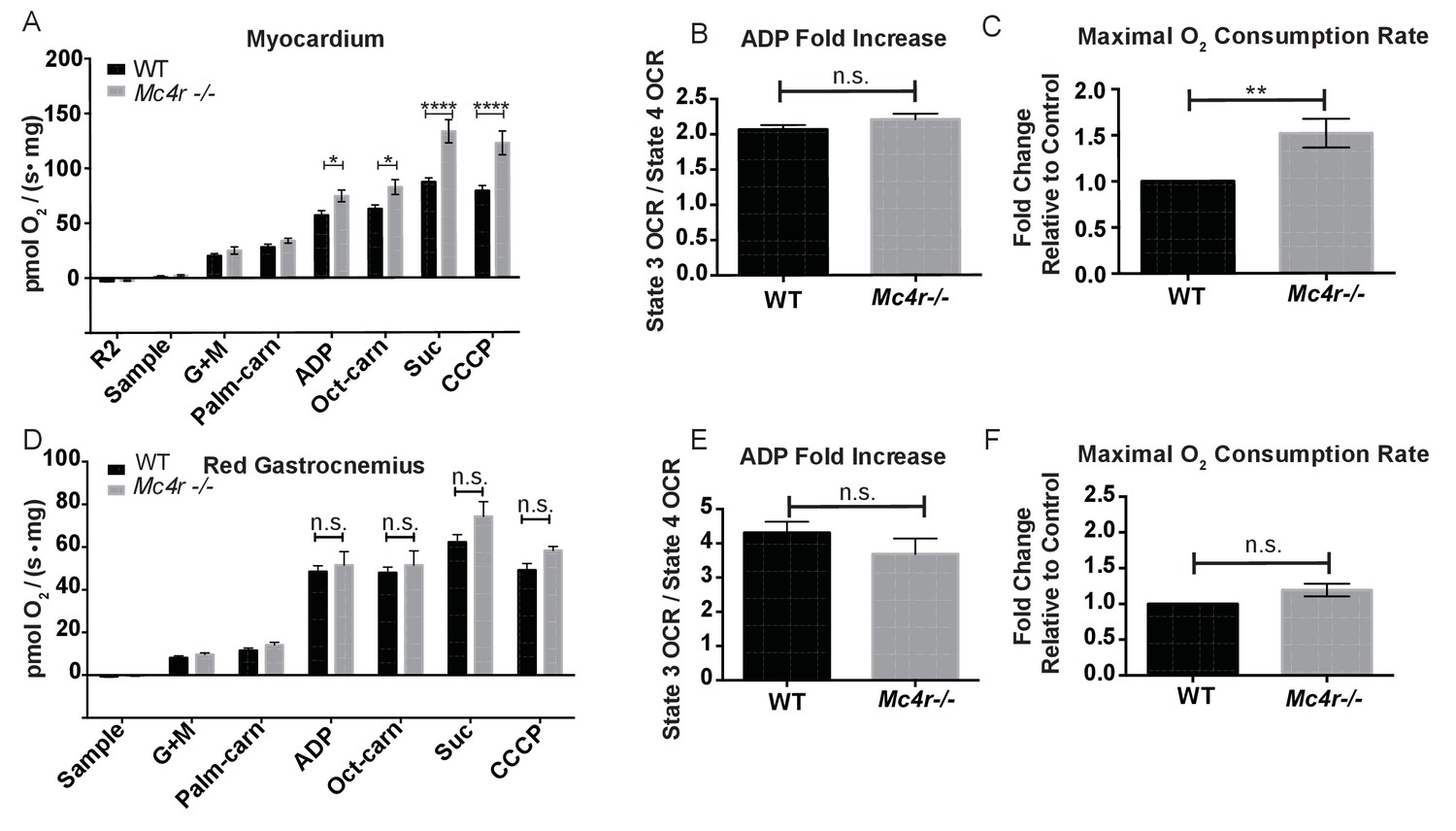
Loss of the melanocortin-4 receptor in mice causes dilated

JCI - Melanocortin 4 receptor signals at the neuronal primary

Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors require an arcuate-to

Controlling Horizontal Cell-Mediated Lateral Inhibition in

Divergence of Melanocortin Pathways in the Control of Food Intake
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)