Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) causes the vast majority of skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) in humans. S. aureus has become increasingly resistant to antibiotics and there is an urgent need for new strategies to tackle S. aureus infections. Vaccines offer a potential solution to this epidemic of antimicrobial resistance. However, the development of next generation efficacious anti-S. aureus vaccines necessitates a greater understanding of the protective immune response against S. aureus infection. In particular, it will be important to ascertain if distinct immune mechanisms are required to confer protection at distinct anatomical sites. Recent discoveries have highlighted that interleukin-17-producing T cells play a particularly important role in the immune response to S. aureus skin infection and suggest that vaccine strategies to specifically target these types of T cells may be beneficial in the treatment of S. aureus SSTIs. S. aureus expresses a large number of cell wall-anchored (CWA) proteins, which are covalently attached to the cell wall peptidoglycan. The virulence potential of many CWA proteins has been demonstrated in infection models; however, there is a paucity of information regarding their roles during SSTIs. In this review, we highlight potential candidate antigens for vaccines targeted at protection against SSTIs.
Lg Download Software V1.3.6.3 - Colaboratory
Pathogen CK-12 Foundation
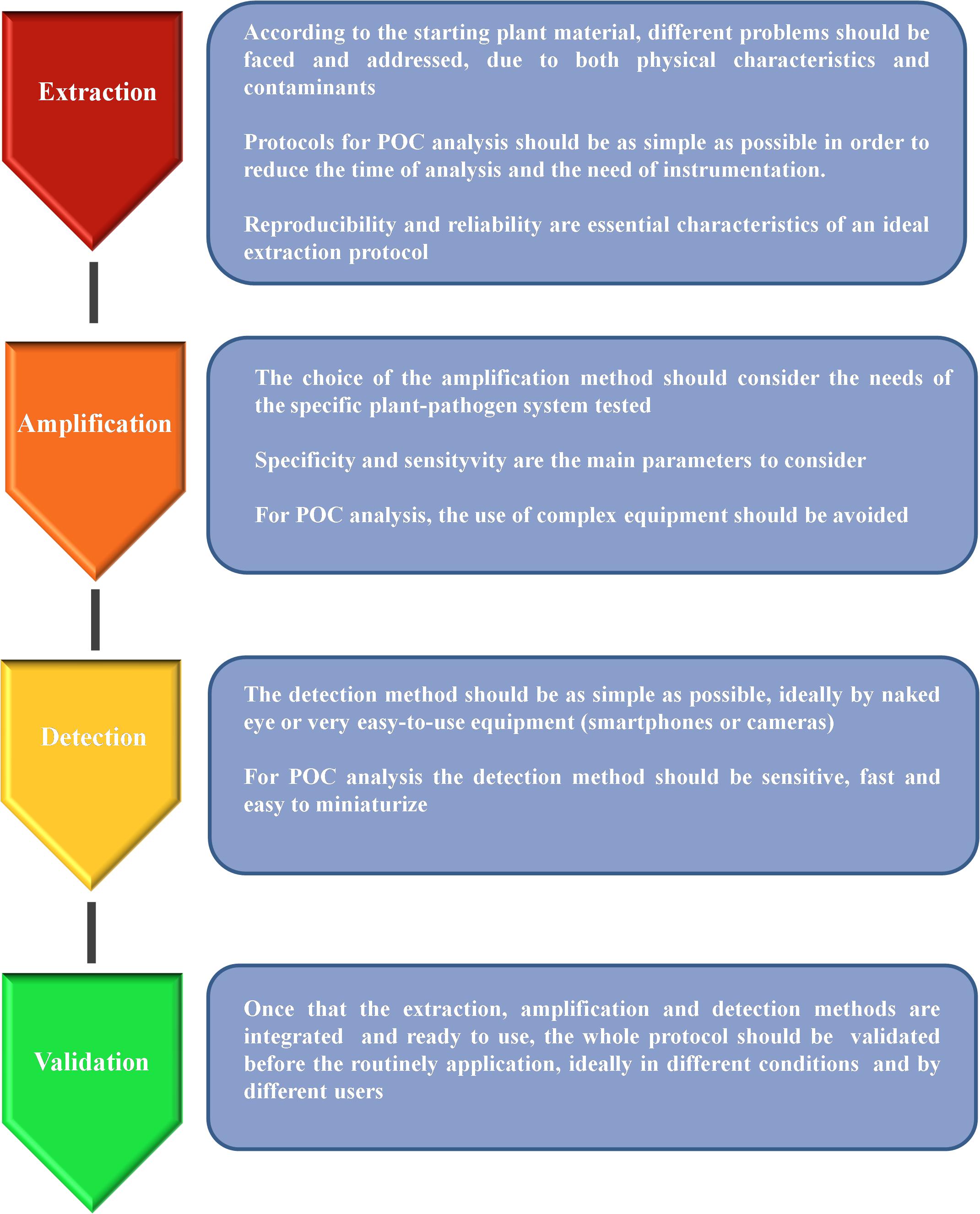
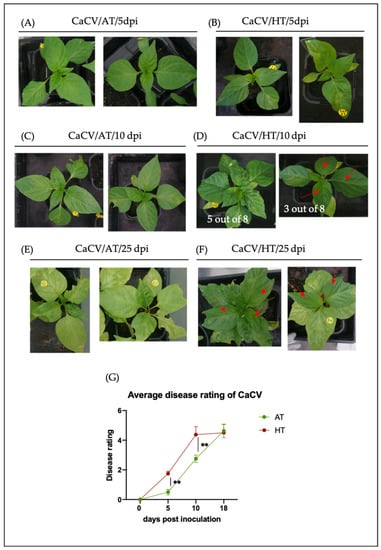
Frontiers Molecular Approaches for Low-Cost Point-of-Care Pathogen Detection in Agriculture and Forestry

Pathogenic bacteria - Wikipedia

Effect of sequential UV/free chlorine disinfection on opportunistic pathogens and microbial community structure in simulated drinking water distribution systems - ScienceDirect

Bloodborne Pathogens Handouts, First Aid

Pathogens and Immunity

Read et al. warned us 2015 using chickens (Marek's disease) that using an imperfect 'leaky' vaccine can enhance transmission of highly virulent pathogens; sub-optimal non-sterilizing non-neutralizing
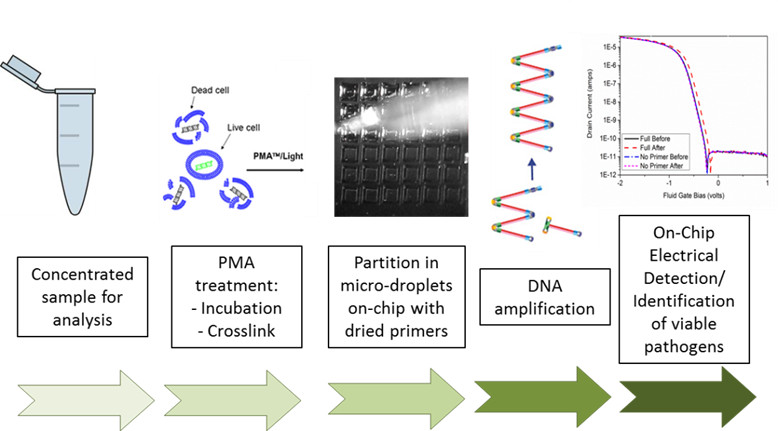
Detection of Viable Pathogens Using Label-Free Electrical Detection of Nucleic Acid Amplification : LIBNA
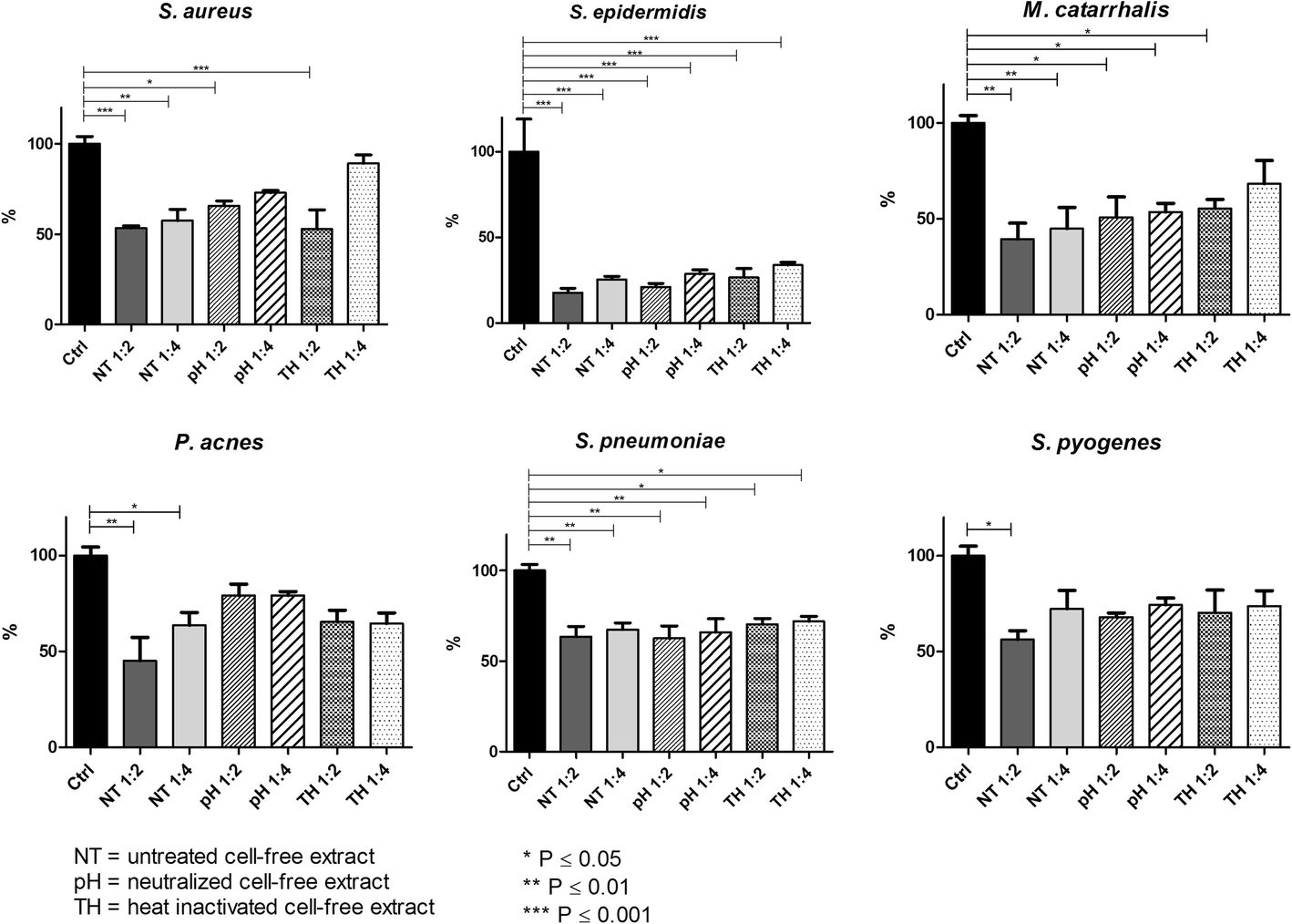
Probiotics Streptococcus salivarius 24SMB and Streptococcus oralis 89a interfere with biofilm formation of pathogens of the upper respiratory tract, BMC Infectious Diseases
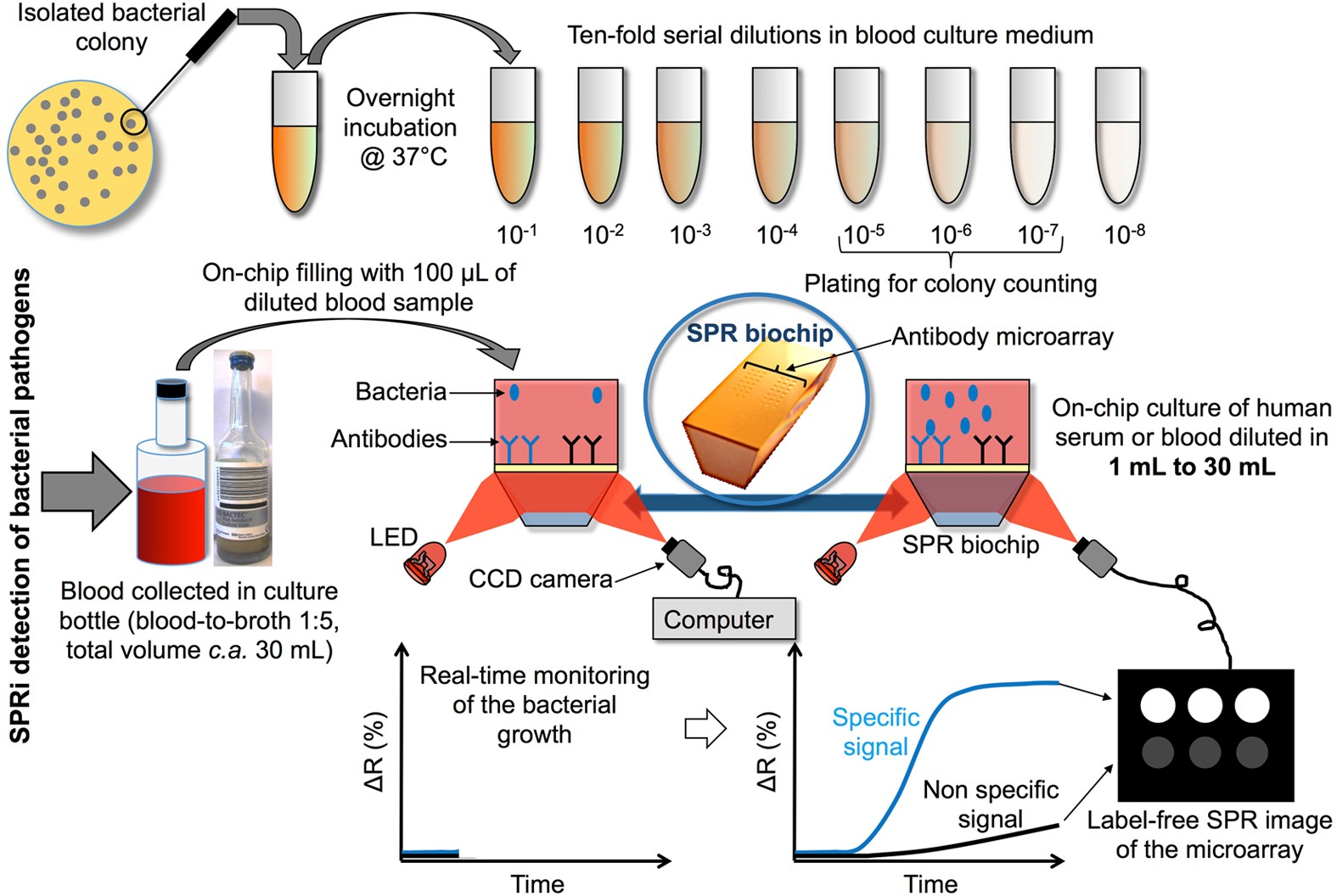
Biochips for Direct Detection and Identification of Bacteria in Blood Culture-Like Conditions
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







