IJGI, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Portraying functional urban areas provides useful insights for understanding complex urban systems and formulating rational urban plans. Mobile phone user trajectory data are often used to infer the individual activity patterns of people and for functional area identification, but they are difficult to obtain because of personal privacy issues and have the drawback of a sparse spatial and temporal distribution. Deep learning models have been widely utilized in functional area recognition but are limited by the difficulty of acquiring training samples with large data volumes. This paper aims to achieve a fast and automatic identification of large-scale urban functional areas without prior knowledge. This paper uses Nanjing city as a test area, and a self-organizing map (SOM) neural network model based on an improved dynamic time warping (Ndim-DTW) distance is used to automatically identify the function of each building using mobile phone aggregated data containing work and residence attributes. The results show that the recognition accuracy reaches 88.7%, which is 12.4% higher than that of the K-medoids method based on the DTW distance using a single attribute and 7.8% higher than that of the K-medoids method based on the Ndim-DTW distance with multiple attributes, confirming the effectiveness of the multi-attribute mobile phone aggregated data and the SOM model based on the Ndim-DTW distance. Furthermore, at the traffic analysis zone (TAZ) level, this paper detects that Nanjing has seven functional area hotspots with a high degree of mixing. The results can provide a data basis for urban studies on, for example, the urban spatial structure, the separation of occupations and residences, and environmental suitability evaluation.
Frontiers Monitoring Changes and Soil Characterization in Mangrove Forests of the United Arab Emirates Using the Canonical Correlation Forest Model by Multitemporal of Landsat Data
Frontiers Monitoring Changes and Soil Characterization in Mangrove Forests of the United Arab Emirates Using the Canonical Correlation Forest Model by Multitemporal of Landsat Data
IJGI, Free Full-Text
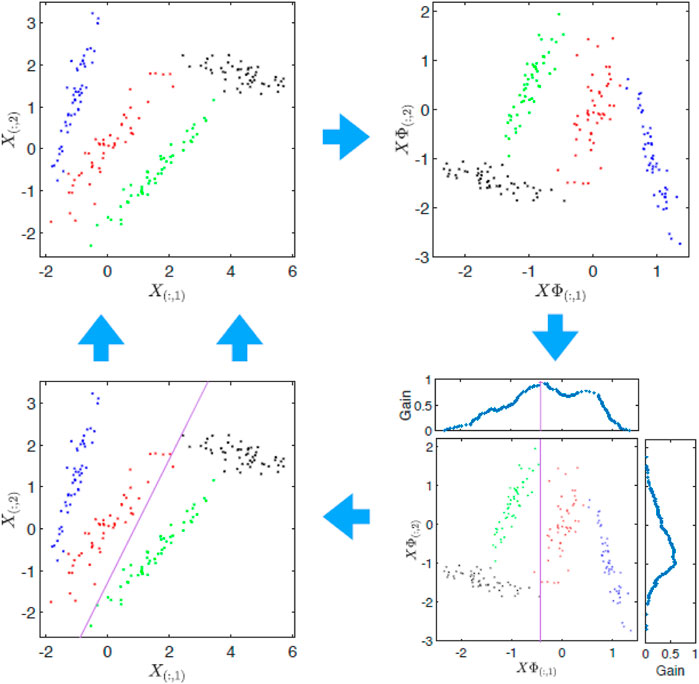
Frontiers Monitoring Changes and Soil Characterization in Mangrove Forests of the United Arab Emirates Using the Canonical Correlation Forest Model by Multitemporal of Landsat Data

MDPI Article Template - Overleaf, Online LaTeX Editor
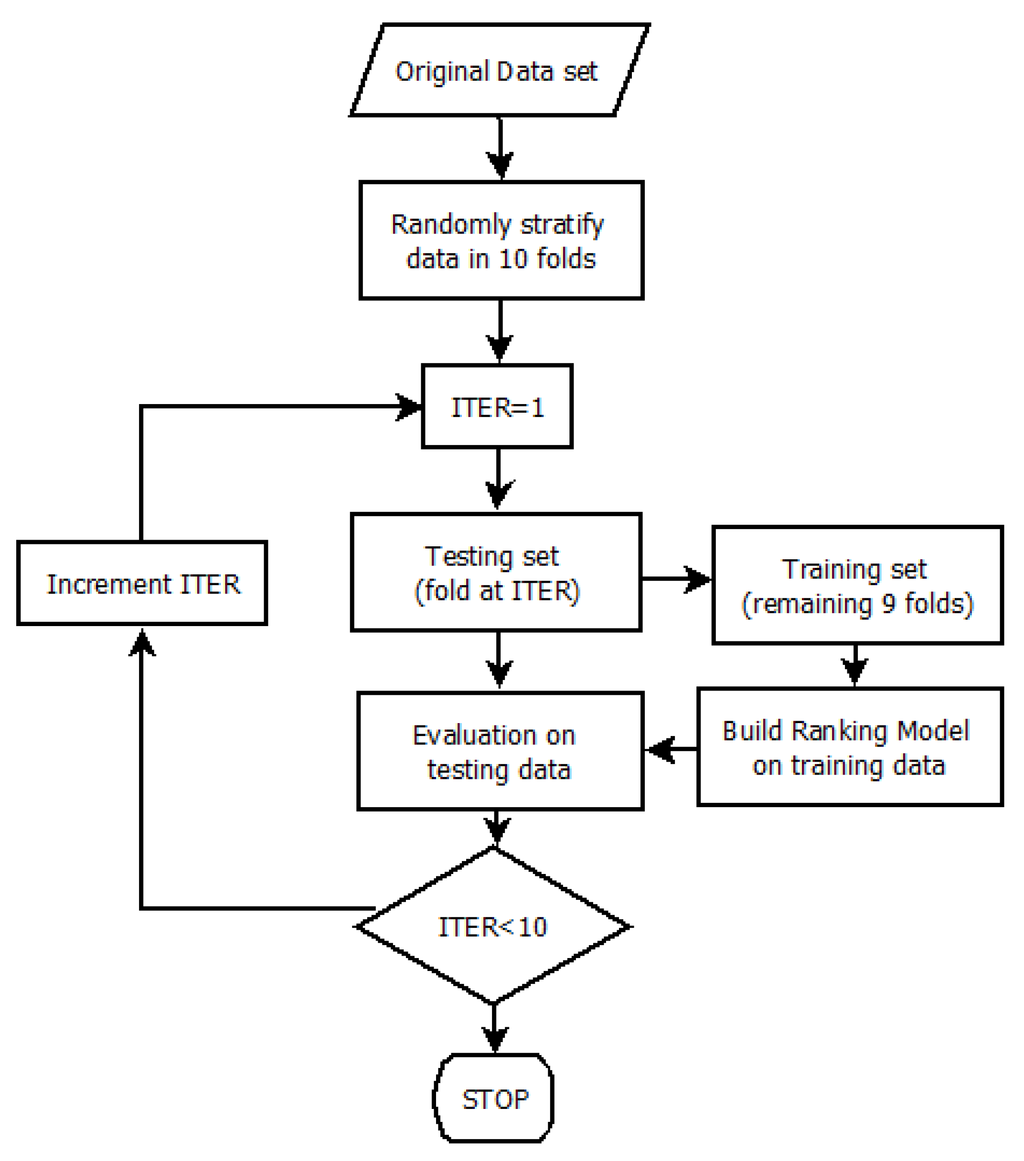
IJGI, Free Full-Text
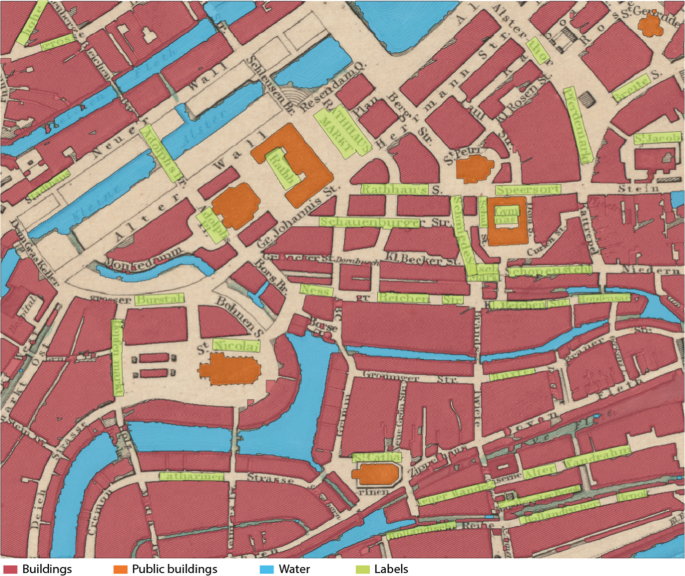
A Holistic Workflow for Semi-automated Object Extraction from Large-Scale Historical Maps
ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information

Full article: A comparison among fuzzy multi-criteria decision making, bivariate, multivariate and machine learning models in landslide susceptibility mapping

PDF) Journal citation reports and the definition of a predatory journal: The case of the Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI)

How to get better search results for tech discovery - Mergeflow
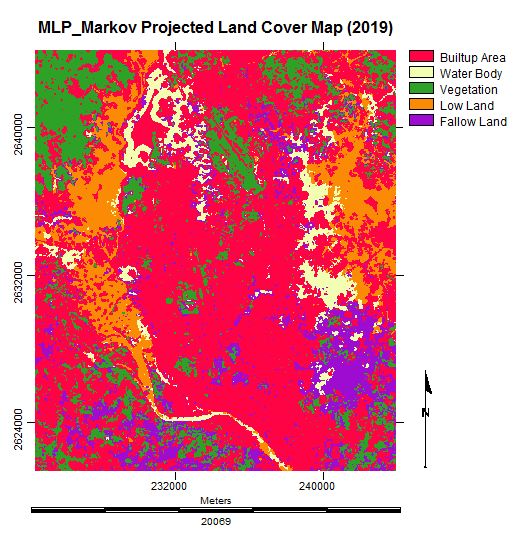
IJGI, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)